January 27, 2012
Current Status of Biomass Power in Japan (2011)
Keywords: Renewable Energy
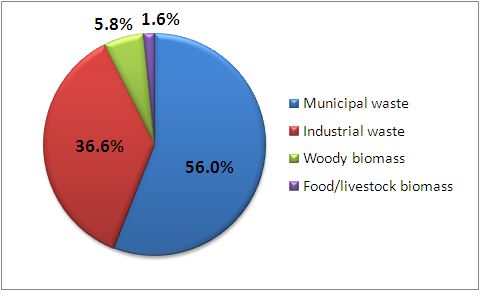
Ratio of Japanese domestic power generation from biomass by source as of March 2010 (installed capacity) *Excluding biomass-coal co-firing power generation
The cumulative installed capacity for power generation from biomass in Japan grew by a little more than 2% over the previous year, with no major changes in the overall current trend, compared to a 7.5-times increase between 1990 and the end of 2009. Power generation from waste accounted for 92.6% of the total, with municipal waste contributing 56% and industrial waste 36.6%.
Biomass power production from wood and food/livestock, which are seen as promising sources of renewable energy at the local level, have also shown a dramatic increase since 2002. However, power production using woody waste from forests remains relatively unchanged at about 6%, highlighting the need for revitalization of the forest industry as well as the cascading use of forestry biomass resources through active utilization of domestic lumber.
References:
- Renewables Japan Status Report 2011 (Japanese):
http://www.re-policy.jp/jrepp/JSR2011/
Back to Current Status of Renewable Energy in Japan
Related
"JFS Newsletter"
- 'Yumekaze' Wind Turbine Project Connects Metro Consumers and Regional Producers: Seikatsu Club Consumers' Co-operative
- Shaping Japan's Energy toward 2050 Participating in the Round Table for Studying Energy Situations
- Nishiawakura's Initiative for 100% Energy Self-Sufficiency, and a Municipal ICO Scheme
- Actions Toward 100% Renewable Energy in Japan
- Sustainable Community Building in Shimokawa: Recycling-Oriented Forest Management Enabling Permanent Use of Forest Resources
Related
"Popular Articles"
- Current Status of Renewable Energy in Japan (2015)
- Offshore Wind Farm Withstands Great East Japan Earthquake and Tsunami
- Current Status of Renewable Energy in Japan (2014)
- Geothermal Power: Japan Has World's Third Largest Geothermal Reserves, 60 Percent of Which Can Be Developed
- Tokyo Plans to Increase Renewable Energy Ratio to 20% by 2024


