January 27, 2013
Japanese Municipalities with Ambitious Targets to Reduce CO2/GHG Emissions
Keywords: Climate Change Local government
While national governments fail to set proactive targets to fight climate change, municipal governments in Japan and in many countries around the world are setting aggressive targets and attempting to reduce carbon dioxide (CO2) or greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. JFS would like to collaborate with and stimulate these forward-looking efforts in Japan and overseas.
If you know of ambitious targets of municipalities not included in this list, please share the information with us and provide a web link (URL) to the source, using this online form. We will review information received and add it to the list.
* We added Yamanashi with its ambitious target.
Source: The City Climate Catalogue (2013/01/27)
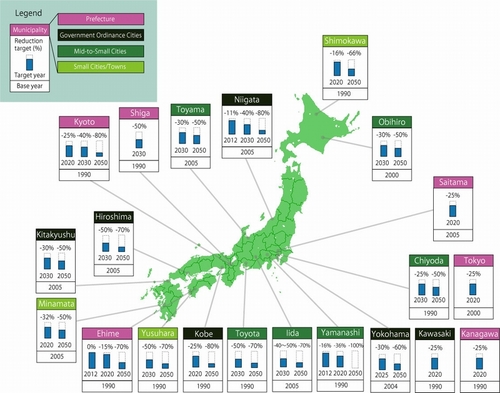
| Municipality (Prefecture) |
Reduction target | Target year | Base year | CO2/ GHG |
Action plan | Established year |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Saitama | -25% | 2020 | 2005 | GHG | Stop Global Warming Saitama Navigation 2050(Summary) | 2008 |
| Tokyo | -25% | 2020 | 2000 | GHG | Source (Japanese only) | 2006 |
| Kanagawa | -25% | 2020 | 1990 | GHG | Source (Japanese only) | 2009 |
| Shiga | -50% | 2030 | 1990 | GHG | Source (Japanese only) | 2008 |
| Kyoto | 1. -25% 2. -40% 3. -80% |
1. 2020 2. 2030 3. 2050 |
1990 | GHG | Source (Japanese only) | 2011 |
| Ehime | 1. -0% 2. -15% 3. -70% |
1. 2012 2. 2020 3. 2050 |
1990 | GHG | Source (Japanese only) | 2009 |
Government Ordinance Cities * City with a population greater than 500,000
| Municipality (Prefecture) |
Reduction target | Target year | Base year | CO2/ GHG |
Action plan | Established year |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yokohama (Kanagawa) |
1. -30% 2. -60% |
1. 2025 2. 2050 |
2004 | GHG | Yokohama Climate Change Action Policy(CO-DO30) Leaflet in English | 2009 |
| Kawasaki (Kanagawa) |
-25% | 2020 | 1990 | GHG | Source (Japanese only) | 2010 |
| Kobe (Hyogo) |
1. -25% 2. -80% |
1. 2020 2. 2050 |
1990 | GHG | Source (Japanese only) | 2011 |
| Nigata (Nigata) |
1. -11% 2. -40% 3. -80% |
1. 2012 2. 2030 3. 2050 |
2005 | CO2 | Source (Japanese only) | 2009 |
| Hiroshima (Hiroshima) |
1. -50% 2. -70% |
1. 2030 2. 2050 |
1990 | GHG | Source (Japanese only) | 2009 |
| Kitakyusyu (Fukuoka) |
1. -30% 2. -50% |
1. 2030 2. 2050 |
2005 | GHG | Source (Japanese only) | 2009 |
Mid-to-Small Cities
| Municipality (Prefecture) |
Reduction target | Target year | Base year | CO2/ GHG |
Action plan | Established year |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Toyama (Toyama) |
1. -30% 2. -50% |
1. 2030 2. 2050 |
2005 | CO2 | Source (Japanese only) | 2009 |
| Toyota (Aichi) |
1. 30% 2. -50% |
1. 2030 2. 2050 |
1990 | CO2 | Source (Japanese only) | 2009 |
| Obihiro (Hokkaido) |
1. -30% 2. -50% |
1. 2030 2. 2050 |
2000 | GHG | Source (Japanese only) | 2009 |
| Iida (Nagano) |
1. -40 to -50% 2. -70% |
1. 2030 2. 2050 |
2005 | GHG | Source (Japanese only) | 2009 |
| Chiyoda (Tokyo) |
-25% | 2020 | 1990 | GHG | Source (Japanese only) | 2009 |
| Yamanashi (Yamanashi) |
1. 15.9% 2. 36.4% 3. 100% |
1. 2012 2. 2020 3. 2050 |
1. 1990 2. 2005 |
CO2 | Source (Japanese only) | 2009 |
Small Cities/Towns
| Municipality (Prefecture) |
Reduction target | Target year | Base year | CO2/ GHG |
Action plan | Established year |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minamata (Kumamoto) |
1. -32% 2. -50% |
1. 2020 2. 2050 |
2005 | GHG | Source (Japanese only) | 2009 |
| Yusuhara (Kochi) |
1. -50% 2. -70% |
1. 2030 2. 2050 |
1990 | CO2 | Source (Japanese only) | 2009 |
| Shimokawa (Hokkaido) |
1. -16% 2. -66% |
1. 2020 2. 2050 |
1990 | CO2 | Source (Japanese only) | 2009 |
Related
"JFS Newsletter"
- Shaping Japan's Energy toward 2050 Participating in the Round Table for Studying Energy Situations
- Implementation of the Paris Climate Agreement: A Report on Japan's Round Table for Studying Energy Situations
- Auto Sales Industry Cooperates to Tackle Social Responsibility: Examples from Yamagata, Japan
- Yokohama FC: Leader in Eco-Activities through Football-Related Carbon Offset
Related
"Popular Articles"
- Large Ozone Hole Observed Again in 2011
- Japan's Pro Baseball Teams Start Eco-Project to Cut Energy Use by 6%
- Manufacturer Saving Energy by Growing Vertical Gardens on Factory Walls
- Sony Draws Up 'Road to Zero' Plan for Zero Environmental Footprint
- Tokyo Announces Innovative 10-Year Strategy against Climate Change