August 24, 2010
Current Status of Renewable Energy in Japan (2010)
Keywords: Renewable Energy
Efforts to introduce renewable energy have begun to accelerate worldwide. These forms of energy do not promote climate change and are important from an energy security perspective. What's the situation with renewables in Japan?
JFS will look at different types of renewables: solar photovoltaic (PV), wind, geothermal, small hydropower (excluding large hydro), and biomass (including waste power generation). In Japan, these forms of energy are sometimes called natural energy, but we will refer to them as renewables.
First, let us examine how much of each type of renewable energy is generated domestically, and its proportion of total power generated in Japan. What is your reaction when you see these numbers?
| Renewable Type | Power Generation (GWh) | Percent |
| Solar Photovoltaic (PV) | 2,311 | 0.2% |
| Wind | 3,248 | 0.3% |
| Geothermal | 2,765 | 0.2% |
| Small-Scale Hydropower | 17,236 | 1.5% |
| Biomass | 11,545 | 1.0% |
| Total | 37,104 | 3.2% |
The above figures were calculated based on the following:
- Solar photovoltaic: Calculated based on a 12% utilization rate of total capacity; JPEA domestic shipments were used to estimate total capacity.
- Wind: Calculated based on a 20% utilization rate of total capacity; NEDO data collated by JWPA to estimate total capacity.
- Geothermal: Figures from "Current Status and Trends in Geothermal Power", published by the Thermal and Nuclear Power Engineering Society (2008).
- Hydropower: Calculated based on a 61% utilization rate of total capacity; facilities included come from the "Hydropower Stations Database", published by the Japan Electric Power Civil Engineering Association. Included power stations are the conduit/run-of-river type and pondage type stations with maximum generation capacity of up to 10,000 kW, and Renewable Portfolio Standard (RPS) eligible facilities.
- Biomass: Calculated based on a 70% utilization rate of total capacity, assuming that 60% of fuel is biomass. Included power stations were RPS eligible facilities with a biomass ratio of about 60% or greater. Energy source breakdown is as follows: general waste power generation (55%), industrial waste power generation (40%), food/livestock biomass (1%), woody biomass (4%).
*Total Power Generation in Japan: Includes major electric power utilities, other electric power producers, and in-house power generation. ("EDMC Handbook of Energy & Economic Statistics in Japan (2010)")
The graph below shows proportions of overall domestic energy generation, by source.
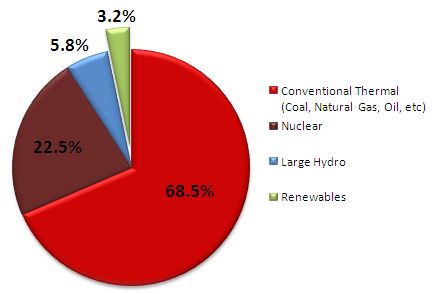
Proportions of Energy Generated, by Source (2008)
Figures for renewables were calculated based on the "Renewables Japan Status Report 2010." Other figures were calculated based on the "EDMC Handbook of Energy & Economic Statistics in Japan (2010)"
In the future, we intend to provide detailed background information and explain the current situation for each type of renewable.
Produced in collaboration with the Institute for Sustainable Energy Policies (ISEP): http://www.isep.or.jp/en/
References:
- Renewables Japan Status Report 2010:
http://www.re-policy.jp/jrepp/JSR2009SMR20091001E.pdf - EDMC Handbook of Energy & Economic Statistics in Japan (2010): http://www.ieej.or.jp/edmc/public/publication-e.html
Go to Current Status of Renewable Energy in Japan (2016)
Related
"JFS Newsletter"
- 'Yumekaze' Wind Turbine Project Connects Metro Consumers and Regional Producers: Seikatsu Club Consumers' Co-operative
- Shaping Japan's Energy toward 2050 Participating in the Round Table for Studying Energy Situations
- Nishiawakura's Initiative for 100% Energy Self-Sufficiency, and a Municipal ICO Scheme
- Actions Toward 100% Renewable Energy in Japan
- Sustainable Community Building in Shimokawa: Recycling-Oriented Forest Management Enabling Permanent Use of Forest Resources
Related
"Popular Articles"
- Current Status of Renewable Energy in Japan (2015)
- Offshore Wind Farm Withstands Great East Japan Earthquake and Tsunami
- Current Status of Renewable Energy in Japan (2014)
- Geothermal Power: Japan Has World's Third Largest Geothermal Reserves, 60 Percent of Which Can Be Developed
- Tokyo Plans to Increase Renewable Energy Ratio to 20% by 2024



