March 21, 2012
Japan, India Joint Project on CDQ System Proves Energy Conservation
Keywords: Environmental Technology Manufacturing industry University / Research institute
Copyright New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization
The New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO) and Japanese steel company Nippon Steel Engineering Co. announced on November 29, 2011, that they held a ceremony marking the completion of the facilities of their joint project called "Model Project for Increasing the Efficient Use of Energy Using a Coke Dry Quenching (CDQ) System." The project has been carried out from FY2006 through FY2011 along with the Indian Ministries of Steel and Finance, and Tata Steel, an Indian steel company.
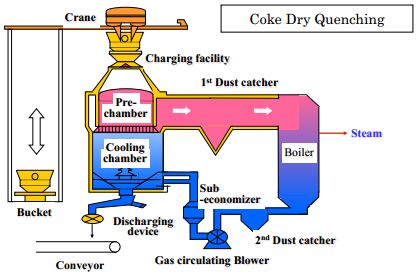
In this project, a CDQ system was installed at Tata Steel's Jamshedpur coke plant. The system cools red hot cokes by inert gas circulation unlike a conventional wet quenching system using water, utilizes recovered heat to generate steam for captive use, and at the same time limits emissions of air pollutants such as coal dust. The collaborative team verified the effectiveness of the new system in terms of energy savings, dust control, and stable blast furnace operations by using homogenized cokes.
The maximum coke disposal rate of the CDQ system is 135 tons per hour. As the system recovers 84 percent of waste heat, energy-saving is reckoned to be equivalent to about 50,000 tons of heavy oil per year, or a reduction of about 137,000 tons of carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions per year. NEDO will promote the spread of the technology throughout India and other nations by providing promotion seminars.
Posted: 2012/03/21 06:00:15 AM
Reference
Energy Efficiency Significantly Improved at a Steel Plant in India
http://www.nedo.go.jp/content/100400210.pdf
Related
"JFS Newsletter"
Related
"Popular Articles"
- New Nano-Bubble Technology May Help Dissolve Sludge and Improve Water Quality
- Japanese Firm Begins Development of Tidal Power Generation System
- Small Hydropower Generation System Developed for Use in Seawater, Weight Cut by Half
- Constructed Wetland Facility Established by Japanese University Purifies Livestock Farming Drainage
- Toyota CRDL Succeeds in World's First Artificial Photosynthesis Using only Water and CO2


