February 20, 2011
NIMS Develops Exhaust Gas Catalyst with 10-fold Greater Thermal Resistance
Keywords: Environmental Technology University / Research institute
Copyright National Institute for Materials Science
National Institute for Materials Science (NIMS) announced, on October 5, 2010, that it had successfully developed an exhaust gas catalyst material with approximately 10 times greater thermal agglomeration resistance. This helps reduce the usage of rare metals such as platinum, palladium and rhodium in catalysts to purify vehicle emissions.
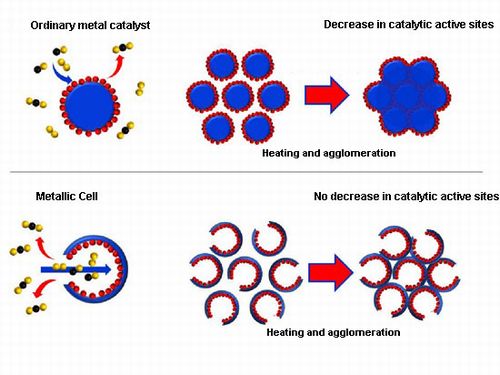
The newly developed material is a platinum sphere (Metallic Cell) synthesized by precipitating a platinum film on the surface of polystyrene powder, followed by heating to 500 degrees Celsius to vaporize the polystyrene. These cells are hollow and approximately 10 micrometers in diameter (1 micrometer is equal to 1/1000 millimeters) containing pores 1 micrometer in diameter that are opened when vaporized gas escapes.
As platinum in conventional catalysts tends to agglomerate when exposed to high temperatures, the active surface area is reduced. As a result, the catalyst loses its catalytic activity. However, the Metallic Cells have catalytic properties on the inside surface, and even when the cells agglomerate, the surface area of the catalyst remains unchanged, as exhaust gas can pass through the pores in the cells.
NIMS stated that the method used to synthesize Metallic Cells can be applied not only to platinum but also to a number of other metals that display catalytic activity. The Institute further stated that the applications of Metallic Cells are not limited to exhaust gas purification technology; they could help reduce the use of rare metals in fuel cell technologies, as well as in other environmental and energy technologies.
Mazda Introduces Single-Nanocatalyst Technology in All-New Mazda3 (Related JFS article)
http://www.japanfs.org/en/pages/028901.html
Posted: 2011/02/20 06:00:15 AM
Reference
Success in Development of Exhaust Gas Catalyst with Thermal Agglomeration Resistance 10x Higher than Conventional Materials
http://www.nims.go.jp/eng/news/press/2010/
10/p201010050.html
Related
"JFS Newsletter"
Related
"Popular Articles"
- New Nano-Bubble Technology May Help Dissolve Sludge and Improve Water Quality
- Japanese Firm Begins Development of Tidal Power Generation System
- Small Hydropower Generation System Developed for Use in Seawater, Weight Cut by Half
- Constructed Wetland Facility Established by Japanese University Purifies Livestock Farming Drainage
- Toyota CRDL Succeeds in World's First Artificial Photosynthesis Using only Water and CO2


