October 21, 2012
Panasonic Develops Artificial Photosynthesis System to Generate Organic Materials from Carbon Dioxide
Keywords: Environmental Technology Manufacturing industry
Copyright Panasonic Corp.
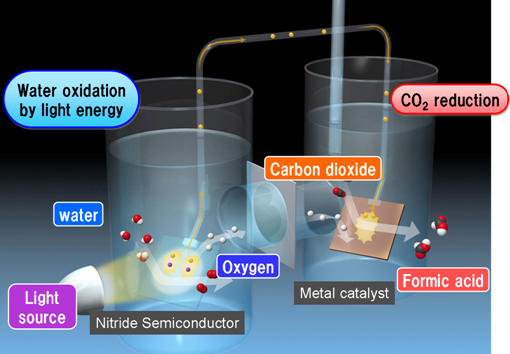
Panasonic Corp., a major Japanese consumer electronics manufacturer, announced on July 30, 2012, that it had developed an artificial photosynthesis system that is able to generate organic materials from carbon dioxide (CO2) and water by illumination with sunlight, similarly to the process that occurs in plants, with the world's highest solar energy conversion efficiency (mentioned as efficiency hereinafter). In this system, emitted CO2 waste is utilized, thus producing chemical raw materials and fuels.
The system uses a nitride semiconductor as a photo-electrode to absorb sunlight and a metal catalyst as an electrode to generate organic materials, achieving an efficiency of 0.2% (major product material: formic acid). This efficiency is comparable to the levels observed in the plants used as a biomass energy source, which require several months to several decades for regrowth.
Related JFS article:
Toyota CRDL Succeeds in World's First Artificial Photosynthesis Using only Water and CO2
Related
"JFS Newsletter"
Related
"Popular Articles"
- New Nano-Bubble Technology May Help Dissolve Sludge and Improve Water Quality
- Japanese Firm Begins Development of Tidal Power Generation System
- Small Hydropower Generation System Developed for Use in Seawater, Weight Cut by Half
- Constructed Wetland Facility Established by Japanese University Purifies Livestock Farming Drainage
- Toyota CRDL Succeeds in World's First Artificial Photosynthesis Using only Water and CO2


